14 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Individuals having vitamin B6 deficiency might notice symptoms like skin rashes, mood swings, tingling sensation and pain in the hands and feet. Several factors such as consuming vitamin B6 inactivating drugs, excessive alcohol, or medical conditions like malabsorption can cause a deficiency.
Stay tuned to know more about the causes and symptoms of this nutrient deficiency and the ways of recovery.
Table of Contents
- What is Vitamin B6 Deficiency?
- How Common is Vitamin B6 Deficiency?
- Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Causes of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Effects of Long-term Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Diagnosis of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- What Should You Eat to Overcome Vitamin B6 Deficiency?
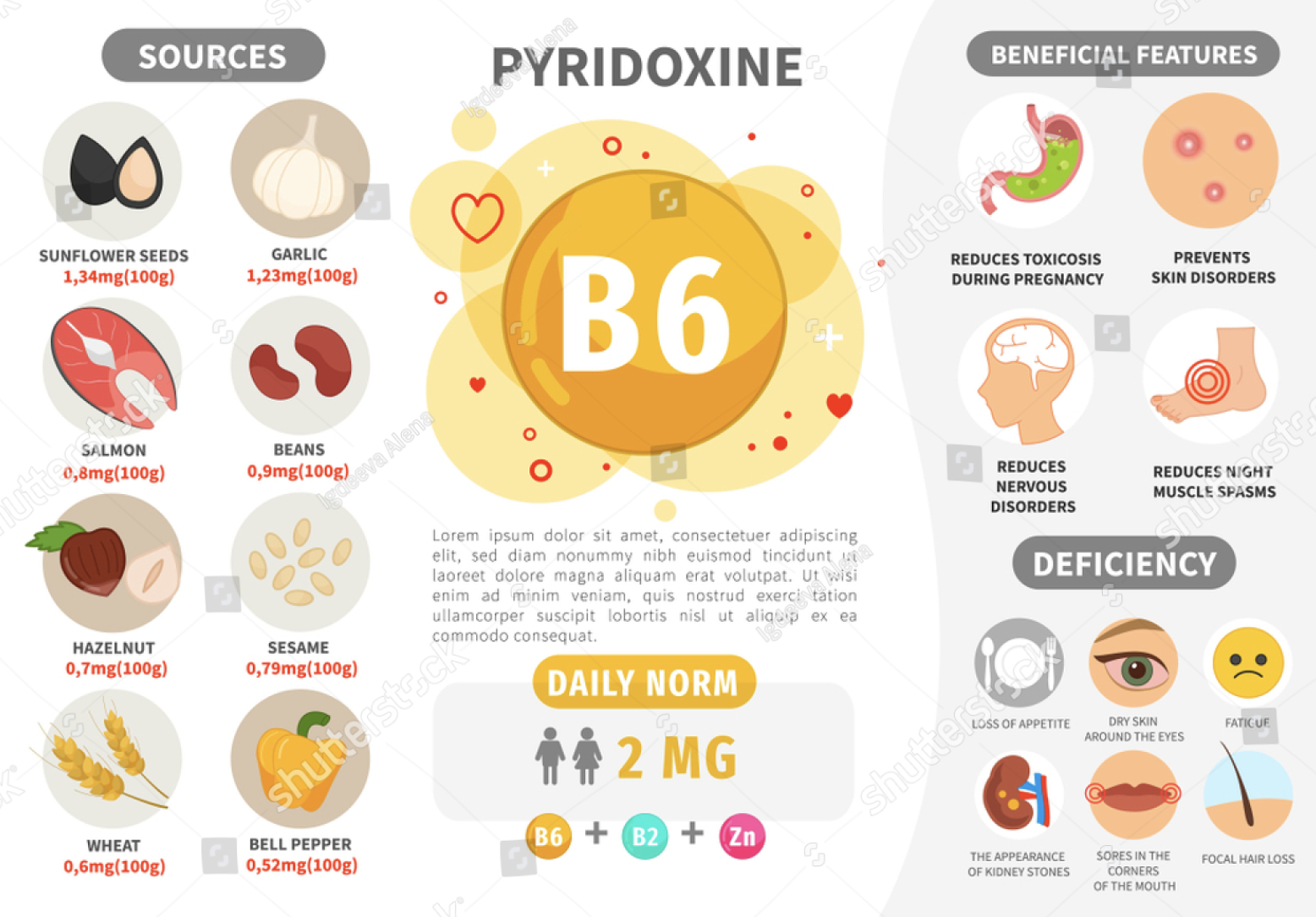
- Best Food Sources of Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B6 Daily Intake
- Diseases Caused by Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Treatment for Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- How to Prevent and Overcome Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Duration to Fix Vitamin B6 Deficiency
- Who is at Risk of Suffering Deficiency
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Vitamin B6 Deficiency?
Vitamin B6 deficiency usually occurs with a low level of other B vitamins, such as vitamin B12 (cobalamin) and vitamin B9 (folic acid). It can cause biochemical changes, becoming more apparent with a gradual increase in deficiency levels.
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is one of the central molecules in cells of a living organism. It is also associated with more than 150 enzymatic reactions as a coenzyme, thus playing a crucial role in the functioning of cells.
How Common is Vitamin B6 Deficiency?
It is rare to have an isolated vitamin B6 deficiency; instead, low levels of other B-complex vitamins, like folic acid and vitamin B12, are typically linked to poor vitamin B6 status. Several variables, including age, food, medical problems, and prescription use, can affect the prevalence. Because fortified meals and dietary supplements are readily available, deficiencies are comparatively uncommon in developed countries.
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
A low level of vitamin B6 can result in the following symptoms –
Symptom Description
Cracked or Sore Lips One major vitamin B6 deficiency symptom is cracked or sore lips. This condition is known as Cheilosis, characterized by red, swollen lips with cracked mouth corners. Individuals may experience bleeding in these areas, leading to infections.
Sore Tongue Inadequacy of pyridoxine can lead to glossitis, marked by a swollen, red, and inflamed tongue. A deficiency of vitamins B6, B9, and B12 can also result in a smooth or glossy tongue due to loss of papillae. Individuals suffering from glossitis have difficulty chewing, talking, and swallowing.
Skin Rashes Symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency in adults include skin rashes. Additionally, individuals with insufficient pyridoxine suffer from red, itchy rashes, called seborrhoeic dermatitis, in particular areas such as the scalp, face, upper chest, and neck.
Mood Changes: Inadequate vitamin B6 impacts one’s Mood and can lead to mental issues like depression, irritability, anxiety, etc.
Low Energy: If an individual feels unusually tired, it might indicate a low level of vitamin B6. One of the primary reasons is that pyridoxine helps make hemoglobin, which further aids in oxygen circulation throughout the body. Insufficient oxygen levels can lead to anemia, resulting in weakness and fatigue.
Weak Immune System A low level of vitamin B6 leads to decreased production of antibodies, white blood cells, and other immune factors essential to prevent infections, inflammations, and various cancers.
Seizures Seizures are one of the common signs of the presence of insufficient vitamin B6 in a body. Individuals can have symptoms like muscle spasms, rolling eyes, jerking in legs and arms, convulsions, and loss of consciousness. However, seizures are more common in infants but can happen in adults.
Tingling Pain When individuals have inadequate vitamin B6, they suffer from nerve damage known as peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms include burning, shooting, and stinging pain in arms, legs, feet, and hands. This medical condition can lead to difficulty walking, clumsiness, and balance problems.
Increased Level of Homocysteine Insufficiency of vitamins B6, B9, and B12 results in increased homocysteine, a by-product of protein digestion. A high level of homocysteine can lead to health issues like heart problems, Alzheimer’s disease, and stroke.
Confusion and Cognitive Impairment: Inadequate levels of vitamin B6 can impair cognitive function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems. This is due to Vitamin B6’s role in neurotransmitter synthesis and brain function.
Weakened Immune Response Vitamin B6 deficiency can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. This includes recurrent infections or prolonged recovery times from illnesses.
Mouth Ulcers Insufficient vitamin B6 can contribute to the development of mouth ulcers or sores inside the mouth. These ulcers can be painful and affect eating and drinking.
Depressed Mood Beyond general mood changes, severe deficiency in vitamin B6 can contribute to more pronounced symptoms of depression. This is due to its involvement in neurotransmitter synthesis, which affects mood regulation.
Difficulty Sleeping Vitamin B6 deficiency may disrupt sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling or staying asleep. This can exacerbate fatigue and affect overall well-being.
The above list thoroughly clarifies which disease is caused by a deficiency of vitamin B6. Now, let us find out what causes this condition.
Causes of Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Vitamin B6 deficiency can occur due to several reasons. Some of them are –
- Malabsorption syndromes, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and ulcerative colitis.
- Individuals with genetic diseases, such as homocystinuria, can cause insufficiency of vitamin B6.
- Certain medications, such as antiepileptic drugs.
- Intake of vitamin B6 inactivating drugs such as antiseizure, isoniazid, hydralazine, and corticosteroids.
- Alcoholism.
- Hyperthyroidism.
Now that you know what causes low vitamin B6, it is time to learn about its long-term effects.
Take a look at the diseases caused by deficiency of vitamin B6.